Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime Crack Free Download
- plaxcabcesigndepi
- Jun 30, 2022
- 7 min read
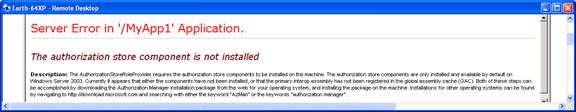
Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime Crack+ Free Download The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime Crack Mac (AMR) is a Windows 2000 Server family version of the Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) API. Windows Server 2003 family operating systems introduced the Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control (RBAC) framework which includes the Authorization Manager API and Role-based MMC snap-in Administration UI (Authorization Manager Snap-in UI is only available on Windows Server 2003 family operating systems and on the Windows Server 2003 Administration Pack for Windows XP.) The Authorization Manager API provides a simplified development model in which to manage flexible groups and business rules and store authorization policies. Storage in Active Directory requires the domain to be at Windows Server 2003 functional level. Using the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime you can build server applications to use the Authorization Manager Role-based access control model that run on Windows 2000 Server family operation systems The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime is a Windows 2000 Server version of the Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) API. Windows Server 2003 family operating systems introduced the Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control (RBAC) framework which includes the Authorization Manager API and Role-based MMC snap-in Administration UI (Authorization Manager Snap-in UI is only available on Windows Server 2003 family operating systems and on the Windows Server 2003 Administration Pack for Windows XP.) The Authorization Manager API provides a simplified development model in which to manage flexible groups and business rules and store authorization policies. Storage in Active Directory requires the domain to be at Windows Server 2003 functional level. Using the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime you can build server applications to use the Authorization Manager Role-based access control model that run on Windows 2000 Server family operation systems Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime Description: The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime (AMR) is a Windows 2000 Server family version of the Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) API. Windows Server 2003 family operating systems introduced the Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control (RBAC) framework which includes the Authorization Manager API and Role-based MMC snap-in Administration UI (Authorization Manager Snap-in UI is only available on Windows Server 2003 family operating systems and on the Windows Server 2003 Administration Pack for Windows XP.) The Authorization Manager API provides a simplified development model in which to manage flexible groups and business rules and store authorization policies. Storage in Active Directory requires the domain to be at Windows Server 2003 functional level. Using the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime Crack + Free The Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager runtime is a Windows 2000 Server version of the Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) API. The Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager runtime delivers the same functionality as the Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager Role-based access control (RBAC) APIs. No client application level code is needed to utilize the Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager runtime. The Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager runtime includes all the functionality of the Windows Server 2003 Authorization Manager RBAC APIs. It provides the following functionality: Provide Role-based access to resources. Authorize users to access resources based on role and group membership. Authorize groups to use resources. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to user groups based on the role and group membership of the user Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to user groups based on the resource authorization group membership. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to user groups based on the resource authorization group membership, and resource assignment. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to user groups based on the resource authorization group membership, resource assignment, and the group membership of the resource assignment user. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to user groups based on the resource authorization group membership, resource assignment, resource assignment user, and the resource user membership. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to user groups based on the resource assignment. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to user groups based on the resource assignment user. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to a resource owner group and resource assignment. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to a resource assignment user. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to a resource assignment and a resource owner group. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to a resource assignment user, and a resource owner group. Authorize a specific resource to be accessible to a resource assignment and a resource owner group, and a resource assignment user. Provide authorization and access to server management applications. Provide reporting of Access Control information. Microsoft offers a Microsoft Software Update Services (SUS) implementation that automatically applies the updates to Windows 2000 Server family operating systems when they are installed. In addition to the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime Activation Code, the following third party products support the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime Cracked Version: Microsoft's Windows 2000 Administration Pack for Windows XP and Windows 2000 Server family operating systems. Microsoft Windows 2000 Server family operating systems and Microsoft Windows 2000 Server Family 91bb86ccfa Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Runtime (AMR) is an application programming interface (API) for Microsoft Windows 2000 Server that provides a simplified development model in which to create flexible groups and run authorization policies. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager (AM) Role-based access control (RBAC) model provides an identity, rights and access-control engine. It supports flexible groups, business rules, and storage in Active Directory (AD). It also provides a role-based Authorization Manager administrative UI that can be used to manage flexible groups and policies. The AMR API is a Windows 2000 Server implementation of the Windows Server 2003 RBAC API. To build applications that use the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Model, you can use any third party programming language supported by the Microsoft Platform SDK (included in Windows Server 2003 family operating system or the Windows Server 2003 Administration Pack for Windows XP). You can use any third party programming language supported by the Windows 2000 programming model. You can use the Microsoft Windows 2000 Authorization Manager API from any Windows programming language supported by the Microsoft Platform SDK. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager API provides access to the following services. These are all services that you would need in order to develop applications which run on a Windows 2000 Server computer. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control (RBAC) Framework: Provides an identity, rights and access-control engine. Flexible groups and access control support the administrative UI Role-based Authorization Manager administrative UI that can be used to manage flexible groups and policies. Using the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager API, you can build server applications that use the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager RBAC model. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based access control model provides a flexible and easy to use platform that allows groups to be created and used by a principal, e.g. an identity. A group represents a collection of principal identities, and grants/denies access to specific operations. The role-based authorization model gives you the flexibility to grant, deny, revoke and add access rights to actions based on both roles and groups. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager (AM) Role-based access control model is comprised of policies, groups and principals. Policies: The authorization policies determine access rights. The Authorization Manager has predefined rights for your group on resources. You can configure access rights and what resources the policy applies to. Groups: The groups represent the group of principals associated with each policy and resource. A group is created and assigned What's New In? Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control Runtime lets you build server applications that use the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager RBAC framework to provide authorization policy for your applications. The Microsoft Identity Manager Windows Server 2008 version of the Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control API is an access control framework that can be used on Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 family of operating systems. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control is also provided as a stand-alone system administration tool for Windows 2000 Server family operating systems. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control is a complete solution for simplifying and reusing business authorization. Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control is based on the Windows 2000 Authorization Manager API which provides: An authorization module to store authorization policies used by applications. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager RBAC Framework for simplifying application development by hiding unnecessary detail for a given authorization policy, and providing more efficient use of storage by automatically applying and removing authorization decisions on a per-entry, per-group basis. Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control Tool Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control Tool provides a user-friendly management UI for Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control Server. Windows 2000 Authorization Manager RBAC Framework for.NET Applications The.NET Framework version 2.0 provides support for Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control. Windows 2000 Authorization Manager RBAC Tool for.NET Applications can be downloaded from: Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control Tool for.NET Applications v2.0 Example of a.NET application to manage role-based access control Provides basic tools to explore the RBAC functionality available in Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control API. Authorization Manager configuration wizard lets you create a new role-based access control policy. Authorization Manager Configuration Wizard runs as a console application and is a Windows 2000 Developer Studio Service Application. Authorization Manager configuration wizard is a one-stop solution for creating a role-based access control policy in Windows 2000 Authorization Manager. Authorization Manager Configuration Wizard is a Windows 2000 Developer Studio Service Application. The Windows 2000 Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control is an access control framework that can be used on Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008 family of operating systems. Authorization Manager Role-based Access Control provides support for simplifying authorization decisions on a per-group, per-entry basis and also features new simplified application development capabilities for System Requirements: DirectX 12, DX12 or Vulkan Windows 7, Windows 8.1, Windows 10 or Windows 10 Mobile Intel Core i3, i5 or i7 processor 4GB RAM or more (8GB recommended) NVIDIA GeForce GTX 750 or better / AMD Radeon HD 4000 or better 32-bit OS and video card Blu-ray Drive & Blu-ray Media Player with free BDMV Video Decoders HDD space of 100GB or more Minimum system requirements for Mac
Related links:

![HD Online Player (cod Rosu La Casa Alba Online Subtitrat 720p Torrent) [HOT]](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/27c70b_c3896f13cb884c4f9a2884ae1efd31a7~mv2.png/v1/fill/w_691,h_524,al_c,q_90,enc_avif,quality_auto/27c70b_c3896f13cb884c4f9a2884ae1efd31a7~mv2.png)


Comments